The modern data stack has taken over legacy systems as the new best practice for data integration, transformation, and management. Its cloud-based infrastructure is more efficient and effective in every category, from extraction to storage to output quality.
Given that this approach is relatively new, there’s much that isn’t widely understood, such as what the various elements of the modern data stack are and how they work together. In this article, we’ll provide a practical example by way of Flux, a fictional personal productivity startup. A behind-the-scenes look at Flux’s operations will illustrate the pain points caused by traditional data infrastructure and how a modern data stack addresses these issues while helping the business run more effectively and in a scalable manner.
What are the components of the modern data stack?
One goal of the modern data stack is to integrate data from every platform used across the company fully. When all data can be queried from a single source, it provides stakeholders with a holistic, real-time picture of business health and performance.
Flux isn’t quite able to achieve this goal using its legacy infrastructure. Preparing reports and visualizations for the weekly executive meeting takes hours. CSVs are exported from SaaS platforms (which may require jumping through several hoops to select the right data), and all the relevant columns are selected and pasted into a “raw data” tab in a spreadsheet. From there, data is cleaned as well as possible — removing duplicates, standardizing formatting, deleting erroneous inputs, etc. — before tables, charts, and analyses can be made. The process is tedious and prone to data integrity issues.
If Flux used a modern data stack instead, its employees could skip right to the analysis step. They would log into their business intelligence (BI) tool, open their “exec meeting dashboard”, and review the recently refreshed tables and graphs.
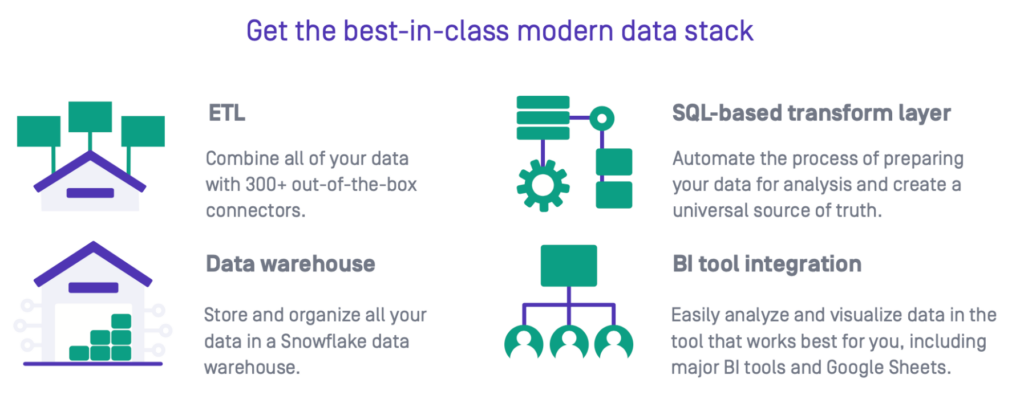
To understand how a modern data stack can drastically truncate this multi-step process, we’ll look at its four main components — all of which are cloud-based, making this an affordable and scalable approach.
Data Extraction
When setting up a modern data stack, all the discrete platforms you want to pull data from get connected to a data warehouse. The data extraction layer will pull raw data sets from each platform according to a preset cadence, such as daily at 7 am. The schedule is defined according to business needs and can be set to refresh some key data more frequently, and other data sets less often.
For example, Flux may decide that certain user behaviors in their personal productivity app should trigger a communication, like an email. This may not be information they only need weekly. On the other hand, they might want to check more frequently for behaviors that they know are correlated with churn.
Data Warehouse
This is the extracted raw data’s first destination. Once in the warehouse, data is cleaned, organized, and stored.
Data Transformation
Once extracted data arrives in the warehouse, it is cleaned and then transformed to prepare it for efficient analysis. Transformation ensures data reliability and enables you to create a single source of truth within the data warehouse.
Business Intelligence
A BI tool is typically the next destination for analysis-ready data. In a BI tool, users can create quick-look dashboards with tables and visualizations of business metrics, set up automated reports to be emailed to stakeholders, and analyze select data sets to extract insights, uncover patterns, and make data-driven decisions.
How do you use a modern data stack?
With its legacy data setup, Flux’s marketing team has a difficult time creating a complete picture of its free users and paid subscribers. The information they need exists in multiple platforms: Flux’s user database maintains a log of in-app behavior, while marketing’s tech stack is completely siloed, with email, social media, and third-party advertising metrics housed in their native platforms. The only way to join the data is to manually extract and organize it within a spreadsheet.
A marketer goes through this process every time they need to answer a business question, such as: When is the optimal time to offer a discount that influences users to upgrade from free to paid? Without combining data from multiple sources, they can only analyze figures in isolation. For example, the analyst can look at timeline details and identify when users who received a discount are most likely to upgrade, but they won’t understand why this is the tipping point. Are the key drivers related to the type of discount, user acquisition channel, engagement with onboarding emails, a particular product feature, number of in-app collaborator connections, or something else?
Combining, cleaning, and organizing all the relevant data sets needed to answer these questions could take days. These manual tasks chip away at employee bandwidth; instead, they could be automated by the modern data stack.
Flux’s marketer would not need to log into each platform to export CSVs. With a modern data stack, extraction would happen behind the scenes at the cadence determined by business needs (for example, daily at 7 am). When marketing, or any other department, needs access to reliable, real-time business metrics, they would simply log into their BI tool.
What are the benefits of a modern data stack?
In addition to the valuable operational improvements illustrated above, businesses quickly achieve five key benefits after transitioning from a legacy system to a modern data stack.
Reliability
Real-time data is cleaned, standardized, and organized within a data warehouse so it can serve as a universal source of truth for all who need to access it.
Accessibility
Reliable data from all departments is available from a single source, and can be accessed by any employee who needs it. This process is also known as data democratization.
Efficiency
Data is accessible on demand, without the need to submit a pull request that would take someone else away from their work. The data work itself is also more efficient when repetitive tasks can easily be automated.
Affordability
While a modern data stack is an investment, there are a few things to consider.
- An all-in-one platform like Mozart Data is likely cheaper than you’d think
- You have some control over costs, determined by how you utilize computing power
- An all-in-one platform like Mozart Data offers savings over assembling a collection of tools with the help of an agency or costly data engineers on the payroll.
Scalability
Storage capacity and computing power can be scaled in parallel, and on-demand, with increased data needs.
How to Create a Modern Data Stack
Setting up the components of the modern data platform can be done in-house, but it’s a time-consuming endeavor that requires technical expertise and would take away resources from other departments. Mozart Data provides an out-of-the-box solution with built-in integrations that enables businesses to get set up quickly and at a fraction of the cost of alternatives. See the platform in action by scheduling a demo with us.